Classification of Cables :
Underground cables are generally classified into two ways:
1) According to the voltage level.
2) According to the insulating material used.
Generally first method of classification is preferred and it is further classified as :
1) Low tension (L.T.) cables = upto 1000v.
2) High tension (H.T.) cables = upto 11.000v.
3) Super lension (S.T.) cables = from 22 kV to 33 kV.
4) Extra high tension (EHT) cables = from 33 to 66 kV.
5) Extra super voltage cables = beyond 132 kV.
1.Low Tension Cables :
First Fig indicate L.T cable Second Fig Indicate HT cable
These cables are generally used for voltages upto 1000 V. These cables can be used for 6600 V also as the electrostatic stress developed in the cable are very small.
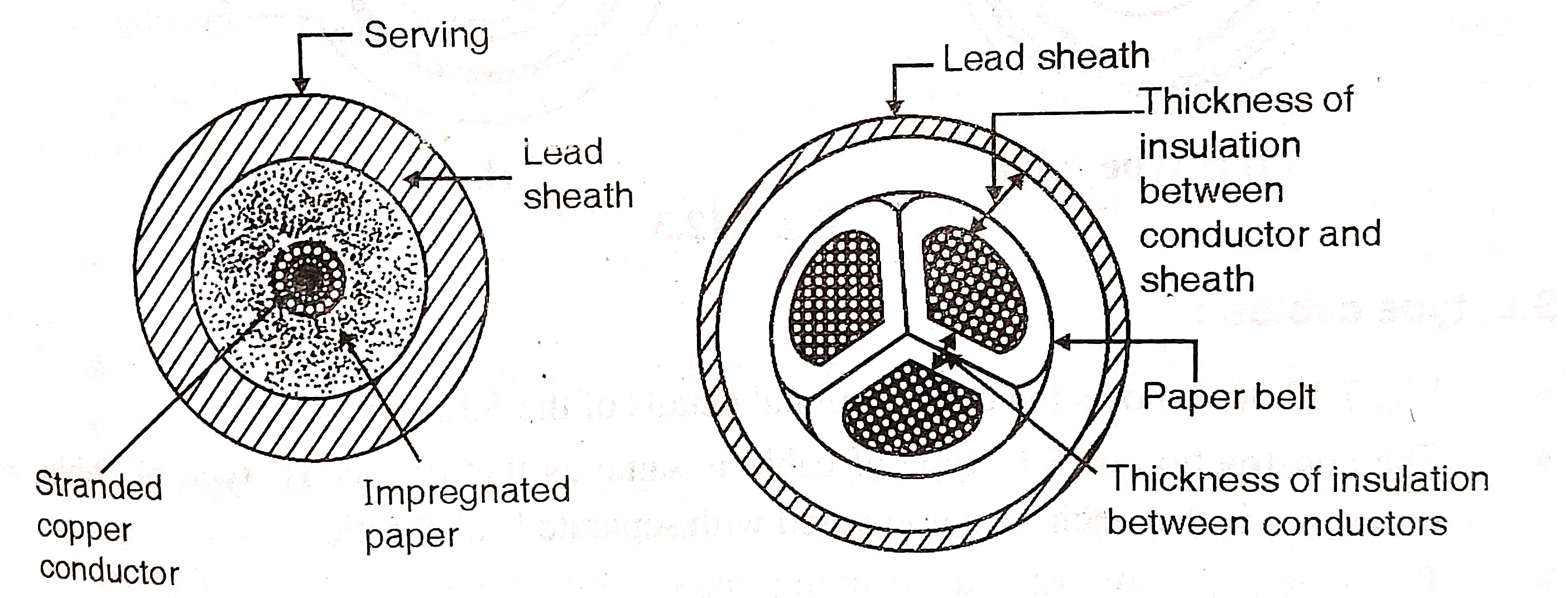
Fig. shows the cross section of a single core low tension (L.T.) cable.
It consists of one circular core of tinned stranded copper (or aluminum) conductors insulated by layers of impregnated paper.
Insulation is surrounded by a lead sheath which protects the cable against moisture.
In order to protect the lead sheath against the corrosion, serving of compounded fibrous material or Hessian tape is provided.
Single core cables are generally not provided with the armoring in order to avoid excessive loss in the armoring
2.High Tension (H.T.) Cables :
Fig. shows the cross sectional view of 3 core belted type High tension (H.T.) cable.
These cables are used upto 11,000 volts.
It consists of three cores of stranded copper (or aluminum conductor).
These three cores are insulated from each other by layers of impregnated paper.
Three insulated cores are bunched together and wrapped with impregnated paper (called as paper belt)
To have a circular cross sectional area the gaps between the insulated core are filled with fibrous insulating material
Lead sheath is wrapped around the paper belt which provides the protection against moisture.
Cable is provided with armoring to protect the cable against the mechanical injury.
Finally serving is provided over the armoring.
These type of construction is not suitable for the voltages above 22,000 volts as both the radial and tangential stresses have to be considered.
The tangential stresses acts along the layers of insulation.
Insulation resistance of layers of paper is quite small therefore tangential stresses setup the
leakage current further which may cause local heating and break down of insulation.
3. Super Tension Cable:
For voltages above 11.000 volts, special construction of cable is required.
Screened cables are used up to 33000 volts in which leakage currents are diverted to earth through metallic sheath.
Screened cables are of two types:
(a) H type cables
(b) S.L type cables
1. H type cables :
These types of cables was invented by H. Hochstadter and hence the name is given.
It consists of three cores and each core is insulated by impregnated paper of desired thickness.
The insulation of each core is covered with the metallic screen which is made up of perforated aluminum foil.
Cores are arranged such a way that each metallic screen makes contact with each other.
Additional conducting tape (made up of cotton with fine wires of copper) is wrapped round all the three cores.
Cable has no insulation belt, but provided with the lead sheath bedding armoring and saving as usual.
As all the four screens and lead sheath are at earth potential, the electric stresses are completely radial also the dielectric losses are reduced.
Another advantages of metal screen is that, heat dissipating capacity of cable increases and there are no sheath losses.
Also, the perforations in the metallic screens assist in the complete impregnation of the cable with the compound and thus the possibility of air pockets and voids in the dielectric is eliminated.
Fig. (a) shows the cross sectional view of 'H' type cable.
(b) S.L. type cables :
Fig. (b) shows the constructional details of the S.L. type of cable.
The construction of S.L. type of cable is same as that of the 'H' type of cable, only the difference is that each core is covered with separate lead sheath.
The three cores are just equivalent to three separate cables.
There is no overall lead sheath but armouring and serving are provided as usual.
Following are the two major advantages of S.L. cable over H type cable :
(a) As each core is provided with separate Iead sheath, it provides less possibility of core to core break down,
(b) Bending of cable becomes easy as there is no overall lead sheath.
The disadvantages of S.L. type of cable is that the great care is required in manufacturing because of thinner lead sheaths.
S.L. types of cables can be used upto 66 KV.
4. Extra High Tension Cables :
The cables considered uptill now are used upto 33 kV and a very limited extent they are used for 66 kv.
These cables are also known as solid cable and there is no extra facility used to increase the dielectric strength and to avoid the possibility of formation of voids.
Thus the solid cables above 66 kV are unsound and owing to development of modern technique it would be impossible to avoid the formation of voids.
When these voids are subjected to electrostatic stresses, ionisation takes place and some times acts as a primary cause of breakdown of cables,
In order to meet the increased voltage demand the extra high tension and extra super voltage power cables useful for 132 kV and 275 kV have been developed.
In above mentioned cables voids have been eliminated by increasing the pressure of compound and that is why such cables are also called as pressure cables,
There are two common types of pressure cables generally used viz : oil filled cables and gas pressure cables,
(i) oil filled cables :
In oil filled cables, ducts or channels are provided in cable for oil circulation.
Fig. (a) shows a single core oil filled cable.
This type of cable consists of oil channel at the center of core by stranding the conductor wires around a hollow cylindrical steel spiral tape.
Oil used for such type of cable is same mineral oil of low viscosity used for impregnation purpose.
The oil is constantly supplied to the channel by means at external oil reservoirs and feeding tanks along its length at certain pressure.
The oil pressure compresses the layer of paper insulation and prevents the possibility of void formation.
The system is so designed that when oil gets expanded due to increase in temperature at
heavy load condition of cable, extra (expanded) oil is get collected in the external reservoir.
When there is fall in temperature during light load condition same oil is sent back during contraction.
The major disadvantage of such type of cable is that complicated jointing system as the channel is at the middle of cable and is at full of voltage with respect to earth.
Fig.(b) shows another type of single core oil filled cable.
In this type of cables, conductor is made similar with solid type of cable and solid insulated oil ducts are provided in the metallic sheath either by grooving the sheath or by arranging the spacers between dielectric and lead sheath.
Fig. (c) shows a cross sectional view of a 3 core oil filled cable
In this type of cable, oil ducts/channels are located within the filling space.
The channels are made up of perforated metal ribbon taking
(ii) Pressure cable :
Constructionally pressure cable is similar to that of an ordinary solid type of cable except that it has triangular shape.
Triangular formation helps to reduce the weight of the cable.
Also the thickness of lead sheath is 75 percent of that of solid type of cable.
Bedding and servings are not provided to pressure cable which helps in decreasing the thermal resistance
But cable is provided with thin layer of armoring. So that the formation of any abnormal ties over its surface is avoided.
Cable is installed in gas tight metal pipes of some what larger area and the pipe is filled with nitrogen gas at a pressure of 12 to 15 atmospheres which continuously
compresses the cable radially from outside so that radial breathing of cable occurs and any voids etc. are closed.